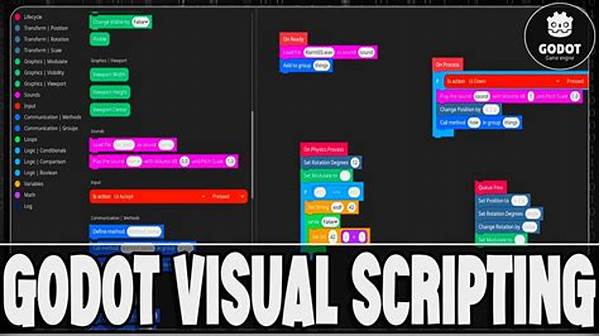
Hey there, fellow Godot enthusiasts! Are you diving into the world of Godot scripting and feeling a bit overwhelmed with all the dos and don’ts? Fear not! You’re about to unravel some nifty tricks that can save you a load of trouble. Godot is a fantastic platform, but like any game engine, it’s essential to follow some best practices to keep your projects running smoothly. Whether you’re a newbie or a seasoned developer, it’s always good to have a refresher on best practices for Godot scripting. So, grab a cup of coffee and let’s jump right in!
Read Now : Licensing Games Made With Free Game Builders
Understanding the Basics
When you start your journey with Godot, familiarizing yourself with its fundamentals is crucial. The best practices for Godot scripting start at the ground level by understanding the engine itself. Get comfortable with nodes, scenes, and how they interact. Godot’s unique scene system can be a bit tricky at first, but once you get the hang of it, it opens up massive creative possibilities. Think of each node as a building block that can be stacked and customized for your game’s needs. By mastering these basics, you’ll set a solid foundation that will help you scale your projects efficiently. It’s this understanding that will guide you in making smart decisions as you progress in your game development journey.
Dive deeper by playing around with Godot’s scripting language, GDScript. It’s straightforward and designed just for this engine, becoming a critical component of our best practices for Godot scripting. Whether you’re implementing game mechanics or managing UI elements, knowing how to leverage GDScript effectively can bring your game to life. Keep your scripts organized and remember, a clean coding environment is a happy coding environment. Debugging becomes ten times easier when you know where things are!
Lastly, don’t shy away from trying out the Godot community resources. The community is incredibly active and there’s no shortage of tutorials and forums where you can seek guidance. Many of the best practices for Godot scripting are often discovered through shared experiences within these circles. People are generous with their knowledge, so utilize it to dodge common pitfalls and enhance your learning curve. Building a network of fellow Godot enthusiasts can really set you up for success as you navigate through your game development quests.
Organizing Your Code
Keeping your scripts neat and tidy is at the heart of best practices for Godot scripting. Clean code is not just about aesthetics; it’s about logic and efficiency. Use comments to annotate your code. Trust me, your future self will thank you! Stick to naming conventions and keep variable names clear and descriptive. Structure your scripts in ways that make them modular and reusable across multiple nodes and scenes. Remember, less is usually more. When modifications or debugging sessions roll around, organized scripts make life way easier. Plus, if you’re working in a team, your colleagues will love you for your neatness!
Embrace Reusability
Incorporating reusable code blocks is another cornerstone in best practices for Godot scripting. Create reusable code snippets and functions to prevent clutter and redundancy. In Godot, you can leverage signals to make your nodes communicate cleanly without falling into the maze of spaghetti code. Once you’ve got a piece of code that you’ll be using multiple times across your project, turning it into a function or a reusable script can save tons of time and headaches. Plus, it keeps your overall project much cleaner and extends the lifespan of your work by having robust, adaptable code.
Optimizing Game Performance
Focus on performance optimizations right from the get-go to ensure smoother gameplay and happier players. Best practices for Godot scripting include regularly profiling your game to identify and reduce bottlenecks. Keep an eye on the polycount, manage asset size, and ensure scripts are running efficiently. Distributed script performance can maximize efficiency, where each node does just what’s necessary, but nothing more. Be rigorous about testing your game on targeted hardware early and often to catch performance issues before they morph into project-crippling nightmares. A well-optimized game is essential not just for performance, but also for scalability.
Testing and Debugging Strategies
Use Godot’s built-in debugging and testing tools to their fullest. This is key in best practices for Godot scripting. Regularly run your game to squash bugs before they multiply and conquer your codebase. Employ breakpoints, inspect variables, and use Godot’s robust error logging to get to the root of issues swiftly. Make testing a fundamental part of your development process. By proactively testing, you drastically decrease the chances of major problems creeping up when it’s least convenient. A rigorous testing strategy builds confidence and stability in your project, promising a robust gaming experience for your audience.
Read Now : Temperature Effects On Composite Strength
Leveraging the Godot Community
The Godot community is like a treasure island just waiting to be explored! One of the best practices for Godot scripting is to connect with other developers. Whether it’s through forums, Discord channels, or GitHub repositories, the wealth of shared knowledge can be invaluable. Many community members generously offer plugins, scripts, and advice that can save you time and avoid development quagmires. Being part of the community can also keep you up-to-date with the latest changes and enhancements in Godot, inspiring your work and enlightening your approach. Collaboration and sharing best practices are a two-way street; as much as you gain, consider contributing back to keep the cycle of support alive and thriving.
Documentation is Key
We can’t stress enough the importance of good documentation. While diving into the best practices for Godot scripting, never overlook the creation of thorough notes for your own project. Godot’s documentation itself is quite robust, but you must also document your projects well. It may seem tedious, but future you will appreciate having documentation to fall back on, especially in larger projects or when you’re bringing new members onboard. High-quality documentation ensures consistent progress and reduces knowledge gaps within your development cycle.
Staying Updated with Godot
Godot is an evolving platform, with new updates rolling out that can offer improved features and functionalities. Best practices for Godot scripting include keeping an eye on release notes and updating your skills accordingly. Newer versions might introduce changes that either enhance your current capabilities or significantly alter existing processes. Staying updated ensures your methodology remains relevant, allowing you to integrate new features or refactor code to match current best practices. This continuous learning loop maintains the longevity and modernity of your projects, aligning them with the latest Godot advancements.
Ending on a High Note
In wrapping things up, remember that best practices for Godot scripting are more of a guide than a one-size-fits-all solution. Every project is unique, and while these practices provide a solid foundation, feel free to adapt them to suit your needs. The beauty of game development lies in its creativity, so while you’re adhering to best practices, always leave room for innovation and experimentation. Keep coding, learning, and, most importantly, having fun with your Godot projects. Don’t stress about perfection; progress is key. Remember, game development is a journey that’s meant to be enjoyed. We hope these best practices help you create something magnificent!
Continuous Learning and Improvement
The world of Godot scripting is vast and continually evolving. Best practices for Godot scripting include staying curious and open to learning. The Godot community is alive with innovation; there’s always something new to discover. Let your projects be playgrounds where you apply these new skills, enhancing both your expertise and the quality of your games. Remember, each script is a stepping stone toward mastery. Learn from each project, adjust your strategies, and carry forward the lessons from challenges faced and solutions found. As you build more, you’ll find your unique rhythm in the symphony of coding, composing games that are as splendid to create as they are to play.